This content is for informational and educational purposes only. Always consult a qualified healthcare provider.
Last Updated on February 2, 2024 by Grace Oluchi
Administering subcutaneous injections can be a challenging task, especially when it comes to children. Children may be afraid of needles or may not understand why they need an injection. However, with the right preparation and technique, subcutaneous injections can be given safely and effectively to children. In this article, we will provide tips and guidelines for parents on how to administer subcutaneous injections.
📋 Table of Contents
What is a subcutaneous injection?
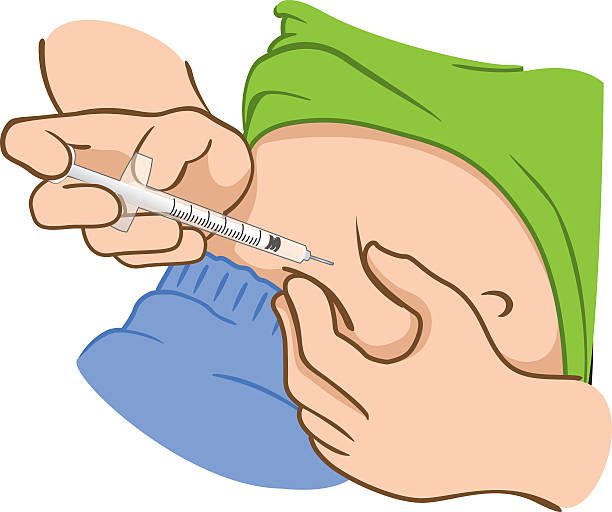
A subcutaneous injection is a type of injection that delivers medication into the layer of fat just below the skin. It is typically given at a 45-degree angle and is used for medications that are absorbed slowly over time. Examples of medications that can be given via subcutaneous injection include insulin and some vaccines.
Overview.
A subcutaneous injection is a type of injection that delivers medication into the layer of fat just below the skin. It’s administration however, is using a small needle and is typically administered at a 45-degree angle. Subcutaneous injections are also in use for medications that slowly absorbs into the bloodstream.
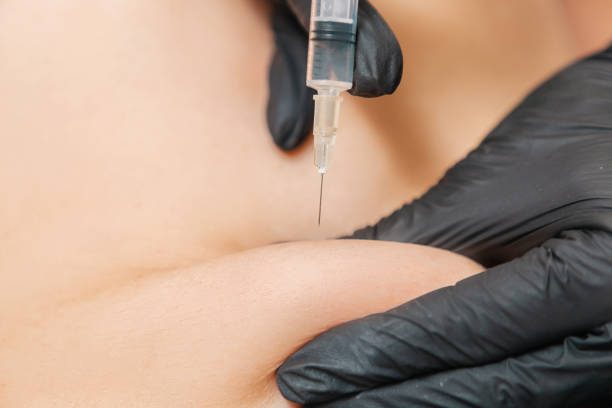

This method of injection is also commonly in use to administer insulin, some vaccines, and other medications. The injection site is usually the upper arm, thigh, or abdomen, and it is important to rotate the injection site to avoid tissue damage. Subcutaneous injections are generally safe and easy to administer, but they can also cause some discomfort or swelling at the injection site.
Medications Given Using a Subcutaneous Injection.
Some examples include:
- Insulin: used to treat diabetes.
- Enoxaparin: an anticoagulant (blood thinner).
- Methotrexate: used to treat cancer, in addition to rheumatoid arthritis, and other conditions.
- Adalimumab: used to treat autoimmune disorders like rheumatoid arthritis, psoriasis, and Crohn’s disease.
- Epinephrine: used to treat severe allergic reactions.
- Growth hormone: used to treat growth disorders.
- Furosemide: a diuretic (water pill) used to treat fluid buildup in the body.
- Vaccines: some vaccines, such as the flu vaccine, can be given as a subcutaneous injection.
How to Administer a Subcutaneous Injection.
To administer a subcutaneous injection, you should follow these steps:
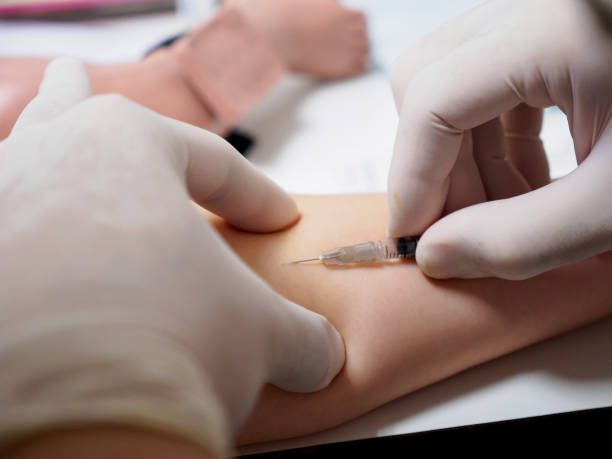

- Wash your hands thoroughly with soap and water.
- Gather all necessary supplies, including the medication, a syringe, and a needle. Additionally, make sure the needle is the appropriate size for the injection and that it is new and sterile.
- Choose an injection site, such as the upper arm, thigh, or abdomen. Clean the area with an alcohol swab and allow it to dry completely.
- Prepare the medication according to the instructions provided by your healthcare provider. This may involve drawing the medication into the syringe and attaching the needle.
- Pinch the skin at the injection site to create a small fold. Insert the needle at a 45-degree angle and push it in until it is fully inserted.
- Slowly inject the medication, also taking care to avoid injecting too quickly or forcefully.
- Once the medication has been injected, remove the needle and apply pressure to the injection site with a clean cotton ball or gauze pad.
- Dispose of the needle and syringe in a sharps container, following your local regulations for proper disposal of medical waste.
- Wash your hands again with soap and water.
Always follow the instructions provided by your healthcare provider for preparing and administering subcutaneous injections. Additionally, it is important to rotate injection sites to avoid tissue damage.
Complications of Subcutaneous Injection.
Complications of subcutaneous injection may include pain, bleeding, infection, allergic reactions, and local tissue damage such as lumps or bumps at the injection site.

In rare cases, subcutaneous injections can also cause nerve damage or damage to be underlying structures such as blood vessels or tendons. It is important to follow proper injection techniques and seek medical attention if any complications occur.
The Key Takeaway.
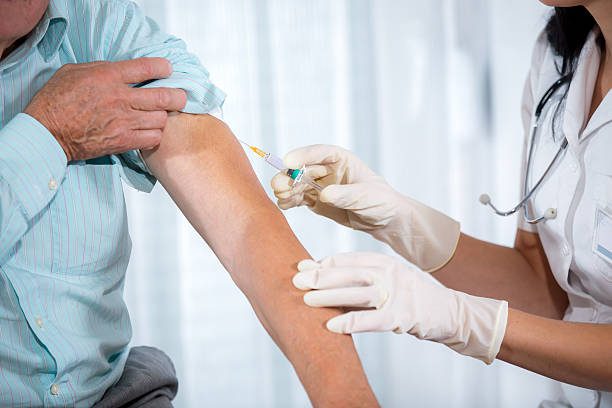

Subcutaneous injections can be an effective route for medication administration. It also is important to follow proper injection techniques to avoid complications such as pain, infection, allergic reactions, and local tissue damage. Seek medical attention if any complications occur.
What is a subcutaneous injection?
A subcutaneous injection is a method of administering medication or vaccines into the fatty layer of tissue just below the skin surface.
What are the common injection sites for subcutaneous injections?
The most common injection sites for subcutaneous injections include the abdomen, the upper arm, and the thigh. However, the exact site of injection may vary depending on the medication being administered and the patient’s age, weight, and health condition.
How is a subcutaneous injection given?
A subcutaneous injection is given using a small, short needle inserted at a 45- to 90-degree angle into the fatty layer of tissue just below the skin surface. The medication is then slowly injected into the tissue.
What are the possible side effects of subcutaneous injections?
Common side effects of subcutaneous injections include pain, swelling, redness, and itching at the injection site. In some cases, more serious side effects such as allergic reactions, infections, and bleeding may occur.