This content is for informational and educational purposes only. Always consult a qualified healthcare provider.
Last Updated on February 2, 2024 by Grace Oluchi
The Babinski reflex is a reflex test used by doctors to evaluate the neurological function of the body, especially in babies. It is a simple test that involves the stimulation of the sole of the foot to observe the response of the toes. In this article, we will answer the top 5 frequently asked questions about the Babinski reflex to help you understand this important neurological test.
📋 Table of Contents
What is the Babinski Reflex?
The Babinski reflex is a reflex test used by doctors to assess the nervous system’s functions in infants and adults. It is a natural reflex that occurs in babies and young children and disappears as they grow older. It is a tool used to detect neurological and muscular abnormalities in the brain and nervous system, and its absence or presence could indicate underlying health conditions.
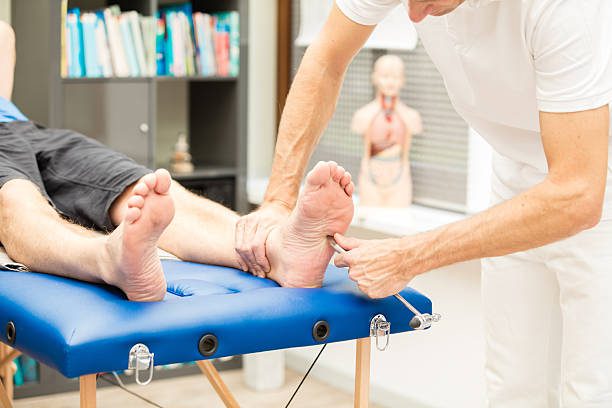

The Babinski reflex is one of the reflex tests that doctors use to assess the neurological functions in infants and adults. Root reflex, suck reflex, grasp reflex, and Moro reflex are other common reflexes that are tested in babies. These reflexes are essential because they indicate healthy neurological function in infants. As children grow and gain better control over their nervous systems, these reflexes disappear.
Joseph Babinski discovered and named the reflex in 1896. Since then, it has become an important tool used by doctors and pediatricians to diagnose neurological conditions. The reflex is tested by stroking the sole of the foot, causing the big toe to bend up and back towards the top of the foot while the other toes fan out. In adults, this response could indicate neurological problems.
How is it Tested?
The Babinski reflex is tested by a doctor. The test involves stimulating the sole of the foot by stroking it with a blunt object or a finger. The doctor strokes the sole of the foot from the heel towards the toes, along the curve of the foot.
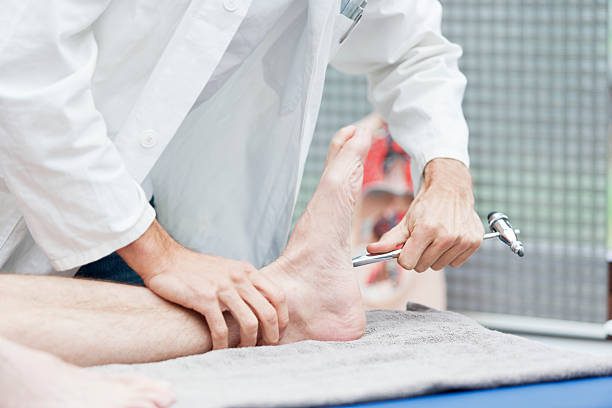

In infants and young children, the normal response to this stimulation is the flexion of all the toes. In contrast, the Babinski reflex in adults is the extension of the big toe and the fanning out of the other toes.
The doctor observes the patient’s foot for any signs of abnormality in the reflex response. The presence of it in adults is abnormal and could indicate basal neurological or muscular disorders.
When is a Babinski Reflex Normal?
The Babinski reflex is considered normal in infants and young children up to the age of two years old. In infants, it is one of many natural reflexes that are present at birth and disappear as the child grows and develops greater control over their nervous system.
During infancy, the nervous system is still developing, and reflexes like the Babinski reflex are important for survival. It also helps infants with walking and crawling by stimulating the muscles in the legs and feet. As a child grows and gains better control over their muscles and nervous system, the Babinski sign disappears, and the normal response changes to the flexion of the toes.
In adults, it is not considered normal. If the Babinski sign is present in adults, it may indicate basal neurological or muscular disorders such as spinal cord injury, brain damage, or other neurological conditions. Therefore, if a Babinski sign is present in adults, it is needful to consult a doctor for proper assessment and diagnosis.
When is it Considered Abnormal?
The Babinski reflex is considered abnormal in adults because it is a sign that disappears as the nervous system matures. In adults, the presence of the Babinski sign indicates an abnormality in the nervous system, such as damage to the brain or nerves.
A doctor will do the babniski reflex test to assess the function of the nervous system in patients with suspected nervous system damage or injury. If the reflex is present, it indicates an abnormality in the corticospinal tract, which is a part of the nervous system that controls voluntary movements.
Babinski sign is commonly seen in conditions such as spinal cord injury, multiple sclerosis, Lou Gehrig’s disease (ALS), cerebral palsy, and brain tumors. Note that the presence of the Babinski sign does not mean that a person has a neurological disorder. It should always be interpreted in conjunction with other clinical findings and diagnostic tests.
In conclusion, the Babinski reflex is considered abnormal in adults and may indicate an basal neurological or muscular disorder. It is important to consult a doctor if you experience abnormal reflexes like the Babinski’s..
Conditions that can Affect the Babinski Reflex.
The Babinski reflex is a neurological test that weighs up the function of the central nervous system. The reflex is normally present in infants but should disappear as they grow older. In adults, the presence of the Babinski reflex may indicate a neurological disorder.
Conditions that can affect the Babinski reflex include:
- Spinal cord injuries.
- Brain injuries.
- Multiple sclerosis.
- Other neurological disorders.
- Certain medications and toxins can also affect the reflex.
The Key Takeaway.
The outlook for individuals with a positive Babinski reflex varies depending on the basal cause. In some cases, treatment of the basal condition may help improve or resolve the Babinski reflex. However, in other cases. The presence of a positive Babinski reflex may be a sign of a more severe neurological condition. And it may require ongoing management.
What is the Babinski reflex?
The Babinski reflex is a reflex test that evaluates the neurological function of the body, specifically the spinal cord and brain. It is also known as the plantar reflex and involves the stimulation of the sole of the foot.
How is the Babinski reflex tested?
The Babinski reflex is tested by a doctor who stimulates the sole of the foot with a blunt object, such as a tongue depressor. The response of the toes is then observed to determine if it is normal or abnormal.
What is the normal response of the Babinski reflex?
The normal response of the Babinski reflex is the curling down of the toes, also known as a negative response. This indicates proper neurological function.
What is an abnormal response of the Babinski reflex?
An abnormal response is the fanning out and upward extension of the toes, also known as a positive response. This may indicate neurological dysfunction and requires further evaluation by a healthcare provider.
When is the Babinski reflex tested?
It is typically tested in infants as part of a routine neurological examination. It may also be tested in adults who have neurological symptoms, such as weakness or numbness in the extremities.

