This content is for informational and educational purposes only. Always consult a qualified healthcare provider.
Last Updated on February 5, 2024 by Grace Oluchi
Vitamin D is essential for bone strength and may support the immune system and other parts of the body.
Getting enough of it can aid in the growth and development of your bones and teeth. Your body produces Vitamin D as a response, when it is exposed to the sun. A person can also boost their boost their Vitamin D intake through certain supplements or food.
📋 Table of Contents
What is vitamin D?
Vitamin D is a fat-soluble vitamin that plays a crucial role in maintaining overall health and well-being. It is unique among vitamins because it can be synthesized by the body when the skin is exposed to sunlight. It can also be obtained through certain dietary sources and supplements.
Sources of vitamin D
There are several sources of vitamin D including:
Sunlight
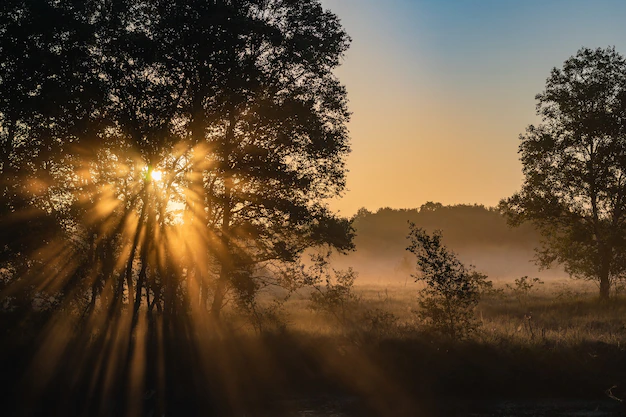


When your skin is exposed to sunlight, it synthesizes vitamin D3 (Cholecalciferol ) in response to sunray.
Spending around 10 to 30 minutes in the sun, a few times a week, with a large area of skin exposed (like your arms, legs, or back), can help your body produce vitamin D. However, the ability of your body to produce vitamin D from sunlight depends on factors such as geographical location, time of day, season, skin pigmentation, and the use of sunscreen.
Fatty fishes contain vitamin D
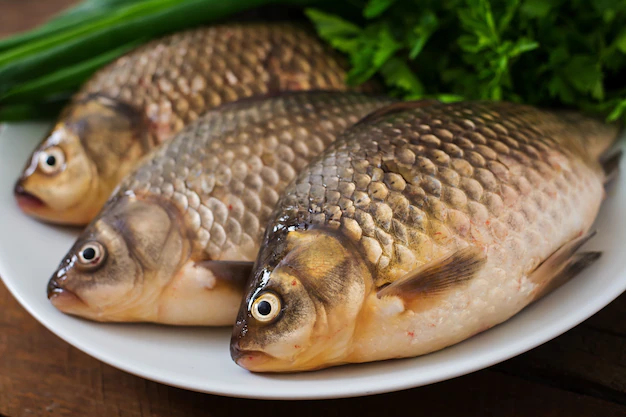


Fatty fishes are excellent sources .Examples include salmon, mackerel, sardines, trout, and tuna. Consuming these fishes can provide a significant amount in your diet.
Cod liver oil contains Vitamin D


Cod liver oil is highly nutritious and it is derived from the liver of codfish. It is a rich source of vitamin D, as well as omega-3 fatty acids. It is available in liquid form or as capsules.
Fortified foods
Many foods are fortified with vitamin D to help increase intake, especially in regions where sunlight exposure is limited. Common fortified foods include milk, orange juice, cereal, yogurt, and plant-based milk alternatives like soy or almond milk. When choosing fortified foods, check the labels to ensure they contain added vitamin D.
Eggs


Egg yolks contain small amounts of it. Adding eggs to your diet can increase your intake of it.
Mushrooms


Some types of mushrooms, particularly those exposed to ultraviolet light during growth or processing, can provide a small amount of vitamin D2. Always make sure you check the packaging or labels to see if the mushrooms have been specifically treated with UV light.
It’s important to note that while these sources can contribute to vitamin D intake, individual requirements may vary. Factors such as age, skin pigmentation, sun exposure, geographical location, and specific health conditions can affect a person’s need of it. If you have concerns about your vitamin D levels, it’s advisable to consult with a healthcare professional for a one on one advice and guidance.
Benefits
It offers numerous benefits to the body. Some key benefits are:
Vitamin D can make your bones stronger
It plays a crucial role in maintaining bone health by enhancing the absorption of calcium and phosphorus from the intestines. This helps in the hardening of bones and teeth, which can help prevent the events of bone weakness in children and adults.
Improved immune function
It is involved in regulating the immune system, and adequate levels are essential for optimal immune function. It helps support the innate and adaptive immune responses, reducing the risk of infections and promoting overall immune health.
Vitamin D may reduce your risk of chronic diseases
Research suggests that sufficient levels of it may help reduce the risk of various chronic diseases. Adequate of intake of it has been associated with a lower risk of certain types of cancers (such as colorectal, breast, and prostate cancer), cardiovascular diseases, autoimmune disorders, and type 2 diabetes.
Enhanced mood and mental health
There is growing evidence linking vitamin D deficiency to mood disorders such as depression, seasonal affective disorder (SAD), and other mental health conditions. So, increasing your intake may help support healthy brain function, improve mood, and reduce the risk of mental health issues.
Vitamin D can aid muscle strength and function
It plays a role in muscle health and is associated with improved muscle strength and function. This is particularly important for older adults, as it can help reduce the risk of falls and improve overall mobility.
Pregnancy and infant health
Sufficient vitamin D levels during pregnancy are important for both the mother and baby. It supports proper fetal skeletal development, reduces the risk of gestational diabetes, preeclampsia, and other pregnancy complications. Additionally, adequate levels of it in infants can contribute to healthy bone growth and immune system development.
Potential anti-inflammatory effects
It exhibits anti-inflammatory properties and may help reduce chronic inflammation in the body. Chronic inflammation is linked to various diseases, including heart disease, diabetes, and autoimmune conditions.
Vitamin D deficiency
There are several factors that can affect your ability to get it from sunlight alone. You may not be able to absorb it due to factors such as the use sunscreen, staying indoors most of the time, living in an area with high pollution ,have a darker skin (high levels of melanin may cause the skin to not get enough of it and live in places where buildings block sunlight
Deficiency symptoms
The majority of people may not experience noticeable signs. However a chronic deficiency may lead to muscle weakness, bone pain, fatigue, mood changes, frequently being ill, hair loss, inability to heal wounds, bone loss and increased fracture risk.
Although, it’s important to note that these symptoms can be caused by various factors, and the lack of it is not the only possible cause. If you suspect a deficiency or experience any of these symptoms, you should consult with a healthcare professional for proper check up and appropriate treatment or supplementation if necessary.
How much of vitamin D do i need?
The recommended dosage can vary depending on factors such as age, health conditions, and individual needs. The following are general guidelines for the recommended daily intake:
Infants (0-12 months): The American Academy of Pediatrics recommends a daily intake of 400 international units (IU) for infants, including breastfed and formula-fed infants.
Children and Adolescents (1-18 years): The recommended daily intake for children and teens is 600-1,000 IU. This can be successful through a combination of sunlight contact, food sources, and supplements if needed.
Adults (19-70 years): The suggested daily intake for adults is 600-800 IU. However, some health organizations suggest higher doses, such as 1,000-2,000 IU, especially for individuals with limited sun exposure, darker skin tones, older age, or underlying health conditions.
Older Adults (over 70 years): Older adults may have reduced ability to synthesize vitamin D from sunlight and may require higher intake. The recommended daily intake for individuals over 70 years is 800-1,000 IU.
Frequently Asked Questions
What happens if I take too much of it?
Even though vitamin D is generally considered safe, too much of it can lead to its toxicity, also known as hypervitaminosis D. This can occur from very high doses of supplements over a long period of time. Symptoms of high intake may include nausea, vomiting, constipation, weakness, feeling thirstier than normal and frequent urination. It’s important to follow the dosage guidelines and seek help from a healthcare professional if you have concerns.
What’s the difference between Vitamin D and Vitamin D3
The thing is both often used in place of the other, but they refer to different forms of the same vitamin. Here’s the difference between the two:
Vitamin D
It is a group of fat-soluble vitamins that includes vitamin D2 (ergocalciferol) and vitamin D3 (cholecalciferol).Which makes it important for various physical functions in the body, such as bone health, immune function, and calcium absorption. It can also be gotten through sunlight exposure, certain foods, and supplements.
Vitamin D3 (Cholecalciferol)
It is a specific form of vitamin D that is naturally produced in the skin when it is exposed to UVB rays from the sun. You can also be get it from animal food sources such as fatty fish, cod liver oil, and egg yolks.
What differentiates the two of them, lies in their sources and how they are gotten. Vitamin D3 is a subtype of Vitamin D, that is primarily synthesized in the skin or gotten from food sources. On the other hand, vitamin D is a broader term that has contains both.
When it comes to supplementation, vitamin D3 is commonly used because it is more digestible and well used by the body compared to vitamin D2. Many vitamin D supplements in the market contain vitamin D3.
Furthermore, it is worth noting that while both forms of vitamins have similar functions in the body, vitamin D3 is generally considered to be more effective in raising and keeping vitamin D levels. However, your choice of supplement intake should be discussed with a healthcare professional, as needs of people may vary based on factors such as health status and existing deficiencies.
Take Away
It’s important to note that while vitamin D is good for your overall health, and too much of it can harmful , which can have adverse effects on your health. Therefore, it’s important that you follow the suggested dosage guidelines and consult with a healthcare professional for advice.