⚠️ Medical Disclaimer
Important: This content is for informational and educational purposes only. It should not be used as a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always consult with a qualified healthcare provider before making changes to your diet, taking supplements, or if you have questions about a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of information you read here.
Last Updated on February 2, 2024 by Grace Oluchi
Once thought to be a disease of the past, gonorrhea is making a comeback – and it’s more dangerous than ever before. The rise of antibiotic-resistant strains of gonorrhea is leading to more and more cases of the disease, which can cause serious health problems if left untreated. To make matters worse, many people don’t even know they have it, as they may not have any symptoms. It’s clear that this disease is a major public health concern.
What is Gonorrhea?
Gonorrhea is a sexually transmitted infection caused by a bacteria called Neisseria gonorrhoeae. This bacteria can infect the genitals, rectum, and throat. This STD is spread through sexual contact, and it can be passed even if the infected person has no symptoms. In fact, many people with this STD don’t know they have it. This is one of the reasons why it can be so dangerous – people can spread it without knowing they have it.


The symptoms of this STD can vary depending on where the infection is located. In the genital area, symptoms may include discharge, pain, or burning during urination. As for the rectum, symptoms may include discharge, itching, or pain during bowel movements. In the throat, symptoms may include a sore throat or a fever. However, many people with it don’t have any symptoms at all. This is why it’s important to test yourself if you think you may have the bacteria.
If left untreated, it can cause serious health problems. In women, it can cause pelvic inflammatory disease, which can lead to infertility, ectopic pregnancy, and chronic pain. In men, it can cause epididymitis, which is an inflammation of the tube that carries sperm from the testicles. The STD can also spread to the blood and joints, causing a life-threatening condition called disseminated gonococcal infection. In addition, it increases the risk of HIV transmission.
How is Gonorrhea Making a Comeback in 2023?
Here’s why the STD is on the rise in 2023:
- First, the bacteria have become resistant to many of the antibiotics that were once effective against it. This means that the infection is harder to treat, and it can cause more severe symptoms.
- Second, there has been an increase in sexual activity without protection, such as condom use. This has led to a higher rate of its sharing.
- Third, there has been a drop in public health funding and education, which has made it harder to prevent and treat the infection.
The increasing prevalence of the STD has a number of serious public health implications.
- First, it can lead to a greater risk of sexually transmitted infections, including HIV.
- Second, it can cause a higher rate of antibiotic resistance, which could lead to a future where no antibiotics are effective against it.
- Third, it can cause more social and economic costs, such as missed work and healthcare costs.
- Finally, it can lead to a loss of public trust in the healthcare system.
Symptoms of Gonorrhea in Men.
Here are the main symptoms of gonorrhea in men, each with a brief explanation:


- A discharge from the penis: The discharge may be watery, yellow, or green in color.
- Pain or burning during urination: inflammation of the urethra, the tube that carries urine from the bladder to the outside of the body.
- Pain or swelling in the testicles: inflammation of the epididymis, the tube that carries sperm from the testicles.
- Fever: Some men with it may develop a fever as their immune system tries to fight off the infection.
- Fatigue: Some men with the STD may feel tired or run down as their body uses up energy to fight the infection.
- Nausea and vomiting: Some men with it may experience nausea and vomiting as a result of the infection.
- Swollen lymph nodes: Some men with it may experience swollen lymph nodes, especially in the groin area.
Symptoms of Gonorrhea in Women.
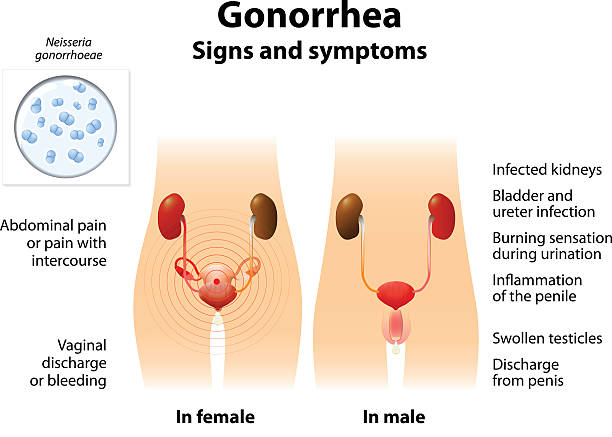

Here’s a list of the main symptoms of gonorrhea in women:
- A discharge from the vagina: The discharge may be watery, yellow, or green in color.
- Pain or burning during urination: Just like with men, the inflammation of the urethra can cause it.
- Pain or bleeding during sex: The inflammation caused by the STD can make sex painful or uncomfortable.
- Bleeding between periods: Some women with it may experience spotting or bleeding in between their regular periods.
- Abdominal pain: it can cause inflammation in the pelvic organs, which can cause pain in the lower abdomen.
- Fever: As mentioned before, some people with it may develop a fever as their immune system fights the infection.
- Nausea and vomiting: Some women with it may experience nausea and vomiting, just like men.
- Irregular periods: it can cause disruptions in the menstrual cycle, leading to irregular periods.
Can Gonorrhea be at Other Sites of the Body?
Gonorrhea can occur at other sites in the body besides the genitals. Let’s go over some of these sites and the symptoms that may occur there:
- The throat: This can cause a sore throat, difficulty swallowing, and a swollen lymph node in the neck.
- The eyes: This can cause redness, swelling, and pain in the eyes.
- The anus: This can cause anal discharge, pain, and bleeding.
The STD at these sites is usually a result of oral or anal sex.
Causes of Gonorrhea.
- Unprotected sex: This is the most common cause of the STD.
- Having multiple sexual partners: The more sexual partners you have, the higher your risk of contracting it.
- Having sex with someone who has it: If your partner has it, you’re at risk of contracting it as well.
- Having sex with someone who has a sexually transmitted infection (STI): People with other STIs are at a higher risk of also having the STD.
One more thing I should mention is that gonorrhea can be passed from mother to child during childbirth. This can cause serious complications for the baby, including blindness. Therefore, it’s important for pregnant women to be tested for this STD and treated if necessary. It can also be passed to a partner even if the person with the STD doesn’t have any symptoms. That’s why regular STI testing is so important.
Risk Factors of Gonorrhea.
- Young age: young people are more likely to have multiple sexual partners, which increases their risk of contracting it.
- Being sexually active: This is the most important risk factor for the STD. The more sexual partners you have, the higher your risk.
- History of other sexually transmitted infections: People who have had other STIs in the past are at a higher risk of contracting it.
- Poverty: People living in poverty are more likely to have limited access to sexual health information and services, increasing their risk of it.
- Drug use: Substance use is associated with risky sexual behavior, including having multiple partners.
- Homelessness: People who are homeless are at a higher risk of it and other STIs, due to limited access to sexual health services.
Complications of Gonorrhea.
There are a number of complications that can occur if the STD is left untreated, including:
- Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID): This is a serious infection of the female reproductive organs, which can cause infertility.
- Epididymitis: This is an infection of the epididymis, a tube that carries sperm from the testicles. It can cause infertility and long-term testicular pain.
- Arthritis: it can cause joint inflammation and pain, which can be debilitating.
- Increased risk of HIV transmission: People with it are more likely to acquire and transmit HIV.
- Inflammation of the heart valves: the STD can spread to the heart valves, causing inflammation and damage.
- Inflammation of the eyes: it can spread to the eyes, causing inflammation and pain.
- Reactive arthritis: This is a type of arthritis that can occur after infection with gonorrhea. It can cause pain and swelling in the joints, eyes, and skin.
How Can You Prevent Gonorrhea?
It’s possible to prevent gonorrhea with the following measures:
- Get tested regularly: Regular testing is important for early detection and treatment.
- Use condoms: Condoms can help prevent the spread of gonorrhea and other STIs.
- Be aware of your partner’s sexual history: Knowing your partner’s sexual history can help you assess your risk of gonorrhea.
- Have an open and honest conversation about STIs: Talking openly and honestly about STIs can help you and your partner make informed decisions about sexual health.
It’s also important to know that there is no vaccine for gonorrhea. However, there are several research projects underway to develop a gonorrhea vaccine. Until a vaccine is developed, the best way to prevent gonorrhea is to practice safe sex. You can also talk to your doctor about the best way to protect yourself from this and other STIs.
How is Gonorrhea Diagnosed?


If you think you may have gonorrhea, your doctor will likely order a test to confirm the diagnosis. Gonorrhea can be diagnosed with a urine test, a swab of the affected area, or a blood test. Your doctor may also recommend testing for other STIs, such as chlamydia. It’s important to be completely honest with your doctor about your sexual history, as this will help them provide the best possible care for you.
Treatment for Gonorrhea.
There are several treatment options for gonorrhea, including:
- Antibiotics: Antibiotics are the main treatment for gonorrhea. Your healthcare provider will likely prescribe a single dose of antibiotics or a course of antibiotics that lasts for several days.
- Antiviral medication: Antiviral medication may be prescribed if you have gonorrhea and another STI, such as HIV.
- Antibiotic resistance: Some strains of gonorrhea are resistant to antibiotics, which means that the antibiotics may not work.
One thing to keep in mind is that it’s important to take all of your antibiotics exactly as prescribed, even if your symptoms go away. Stopping your antibiotics early can lead to the infection coming back, and it can also increase the risk of antibiotic resistance. It’s also important to avoid having sex until you’ve finished your antibiotics and your symptoms have gone away, as this can help prevent spreading the infection to others.
What are the Clinical Trials for Gonorrhea?
There are several clinical trials for gonorrhea, including:
- Vaccine trials: Researchers are currently testing a vaccine that could prevent gonorrhea.
- Antibiotic resistance trials: These trials are looking at new ways to treat gonorrhea that is resistant to antibiotics.
- Prevention trials: These trials are testing new ways to prevent gonorrhea, such as microbicides and other prevention methods.
If you’re interested in participating in a clinical trial, you can talk to your doctor or visit a clinical trial registry website to find a trial that may be right for you.
Does Gonorrhea Have a Cure?
No. While there is no cure for gonorrhea, it can be treated with antibiotics. However, as mentioned before, some strains of gonorrhea are resistant to antibiotics, which means that the antibiotics may not work. In these cases, it’s important to work with your doctor to find an alternative treatment option. It’s also important to remember that even if you’re cured of gonorrhea, you can get it again. The best way to prevent getting gonorrhea is to practice safe sex and to talk to your doctor about testing and treatment.
How Does Gonorrhea Affect Pregnant Women and Infants?
When a pregnant woman has gonorrhea, it can be passed to the baby during childbirth. This can cause serious health problems for the baby, including blindness, meningitis, and blood infections. Treatment for gonorrhea during pregnancy is important to protect the health of the baby. Gonorrhea can also be passed to the baby during breastfeeding. If you’re pregnant or breastfeeding and think you may have gonorrhea, it’s important to talk to your doctor as soon as possible.
Gonorrhea during pregnancy can also cause premature birth and low birth weight. I’d also like to mention that in some cases, gonorrhea can be fatal for infants, so it’s extremely important to get treatment if you think you may have it.
The Key Takeaway.
Gonorrhea is a sexually transmitted infection that can have serious consequences if left untreated. However, it can be treated with antibiotics, and there are several clinical trials underway that could lead to new treatments or even a vaccine in the future. By being aware of the symptoms and risk factors for gonorrhea, and by practicing safe sex, you can help to prevent this infection and protect your health. If you think you may have gonorrhea, it’s important to talk to your doctor provider as soon as possible so that you can get the treatment you need.
FAQs on Gonorrhea.
What are the symptoms of gonorrhea?
The most common symptoms of gonorrhea are a discharge from the vagina or penis, pain or burning during urination, and pain or swelling in the testicles. However, not everyone with gonorrhea has symptoms.
How is gonorrhea transmitted?
Gonorrhea is transmitted through sexual contact, including vaginal, anal, and oral sex. It can also be transmitted from an infected mother to her baby during childbirth.
Can gonorrhea be cured?
No. but it can be treated with antibiotics. However, some strains of gonorrhea are resistant to certain antibiotics, so it’s important to talk to your doctor about the best treatment option for you. It’s also important to take all of the antibiotics as prescribed, even if your symptoms go away before you finish the medication.
Can you get gonorrhea again after being treated?
Yes, you can get gonorrhea again after being cured. It’s important to practice safe sex and to get tested regularly if you’re sexually active.
Can gonorrhea cause infertility?
Yes, untreated gonorrhea can cause infertility in both men and women. In men, gonorrhea can cause scarring of the epididymis, which can lead to a blockage of the tube that carries sperm from the testicles. In women, gonorrhea can cause pelvic inflammatory disease, which can lead to scarring of the fallopian tubes and infertility. It’s important to get treatment for gonorrhea as soon as possible to reduce the risk of infertility.

