This content is for informational and educational purposes only. Always consult a qualified healthcare provider.
Last Updated on February 18, 2024 by Grace Oluchi
Syphilis is a bacterial infection that spreads through sexual contact, blood transfusion, or from mother to child during pregnancy or birth. It’s cause is by a type of bacteria – Treponema pallidum.
📋 Table of Contents
How Do You Get Syphilis?
- Syphilis mainly spreads through oral, vaginal, or anal sex with someone who has the infection. The bacteria can enter the body through small cuts or sores on the skin or mucous membranes.
- You can also get syphilis by sharing needles or other injection equipment with someone who has the infection.
- Syphilis can also spread from a mother to her baby during pregnancy or childbirth. We call this congenital syphilis and can cause serious birth defects or death of the baby.
What Are the Symptoms of Syphilis?
Syphilis has four stages: primary, secondary, latent, and tertiary. The symptoms vary depending on the stage of the infection. But many people with it do not have any symptoms or do not notice them. That is why you have to do regular tests if you are sexually active or have any risk factors.
Primary Syphilis.
The first sign is usually a painless sore called a chancre. It appears at the site where the bacteria entered the body, usually on the genitals, anus, or mouth. The chancre can last for 3 to 6 weeks and heal on its own. And this does not mean that the infection is gone. The bacteria can still spread to other parts of the body or to other people.
Secondary Syphilis.
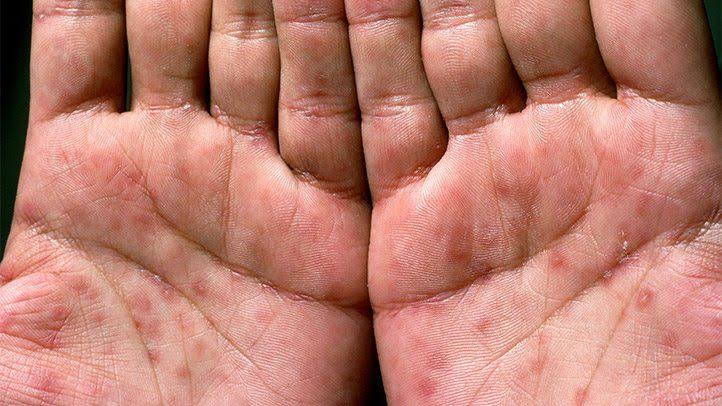
About 2 to 8 weeks after the chancre heals, you may develop a rash on your skin. The rash can be rough, red, or brown and may cover the whole body or just some parts. It often affects the palms of the hands and the soles of the feet. You may also have other symptoms, such as:
- Fever.
- Swollen lymph nodes.
- Sore throat.
- Headache.
- Muscle aches.
- Fatigue.
- Hair loss.
- Wart-like sores in the mouth, genitals, or anus.
These symptoms may last for a few weeks or months and then go away. This does not also mean that the infection is gone. The bacteria can still spread to other parts of the body or to other people.
Latent Syphilis.
This is the stage when you have no symptoms. It can last for years or even decades. During this time, the bacteria can remain dormant in your body and not cause any harm. Note that, they can also become active again and cause serious complications. And you can still pass the infection to others during this stage.
Tertiary Syphilis.
This is the most serious and rare stage of the infection. It occurs when the bacteria damage your organs, such as your brain, heart, eyes, or nerves. This can cause symptoms such as:
- Blindness.
- Deafness.
- Paralysis.
- Dementia.
- Stroke.
- Aneurysm.
- Inflammation of the blood vessels.
- Gummas, which are soft, non-cancerous growths on the skin or bones.
Tertiary syphilis can be fatal if not treated.
How is Syphilis Diagnosed and Treated?
Syphilis can be diagnosed by a blood test or by examining the fluid from a sore.
Syphilis can be cured with antibiotics, usually penicillin. You will need one or more injections of the medicine, depending on the stage of your infection. Avoid sexual contact until your treatment is completed and your sores are healed. You should also inform your sexual partners and tell them to get tested and treated. If you are pregnant, you should get treated as soon as possible to prevent passing the infection to your baby.
How Can You Prevent Syphilis?
- The best way to prevent syphilis is to practice safe sex. This means:
- Using a condom or a dental dam every time you have oral, vaginal, or anal sex.
- Limiting the number of sex partners you have.
- Getting tested and treated for syphilis and other STIs regularly.
- Asking your partner to get tested and treated for syphilis and other STIs before having sex.
- Avoiding sharing needles or other injection equipment with anyone.
The Key Takeaway.
If you have syphilis, you should complete your treatment, avoid sexual contact until you are cured and your sores are healed and inform your sexual partners and tell them to get tested and treated.
FAQs on Syphilis.
Can syphilis cause death?
Yes, it can cause death if not treated. It can damage the brain, heart, eyes, nerves, and other organs. This can lead to blindness, deafness, paralysis, dementia, stroke, aneurysm, inflammation of the blood vessels, or soft, non-cancerous growths on the skin or bones.
Can Syphilis Increase Your Chances To Contacting HIV?
Yes. it can increase the risk of getting HIV, the virus that causes AIDS.
Can syphilis affect pregnancy?
Yes it can affect pregnancy and the baby’s health. It can make it more likely that the baby will be born too early or stillborn. It can also cause the baby to have birth defects or die.
Can syphilis cause blindness?
Yes, it can cause blindness if it affects the eyes. This can happen in any stage of the infection, but it is more common in tertiary syphilis. Syphilis can cause inflammation of the eye (uveitis), damage to the optic nerve (optic neuritis), or abnormal blood vessels in the retina (retinitis). These conditions can lead to vision loss or blindness if not treated.
Can syphilis be transmitted by kissing?
Yes, it can be transmitted by kissing if there is a syphilis sore in or around the mouth. This is rare and very unlikely. The risk is low but not zero.
Can syphilis cause hair loss?
Yes, it can cause hair loss in some people. This is a symptom of secondary syphilis, which occurs 2 to 8 weeks after the initial infection. Syphilis can cause patchy hair loss (alopecia) on the scalp, eyebrows, eyelashes, beard, or other parts of the body. The hair loss is usually temporary and reversible with treatment.
Can syphilis be cured naturally?
No, it cannot be cured naturally. Syphilis requires antibiotics to kill the bacteria and stop the infection. There is no natural remedy or cure for it.
Can syphilis cause mental illness?
Yes, it can cause mental illness if it affects the brain. This is a complication of neurosyphilis, which can occur at any stage of the infection. Syphilis can cause changes in mood, personality, behavior, memory, and cognition. It can also cause psychosis, paranoia, delusions, hallucinations, and dementia. These mental disorders are known as general paresis or syphilitic insanity. They can be treated with antibiotics, but they may cause permanent damage to the brain.
Can syphilis be mistaken for another disease?
Yes, it can be mistaken for another disease because its symptoms is similar to many other conditions. Syphilis is sometimes called “the great imitator” because it can mimic the signs of diseases such as HIV, herpes, gonorrhea, chlamydia, lupus, Lyme disease, and tuberculosis. That is why it is important to get tested regularly.
Can syphilis cause infertility?
Yes, it can cause infertility in both men and women. Syphilis can damage the reproductive organs and cause inflammation, scarring, or blockage of the tubes that carry sperm or eggs. Syphilis can also affect the quality and quantity of sperm or eggs. It can make it harder to get pregnant or cause miscarriage, stillbirth, or birth defects. Now, the treatment for syphilis can improve fertility, but it may not reverse the damage caused by the infection.